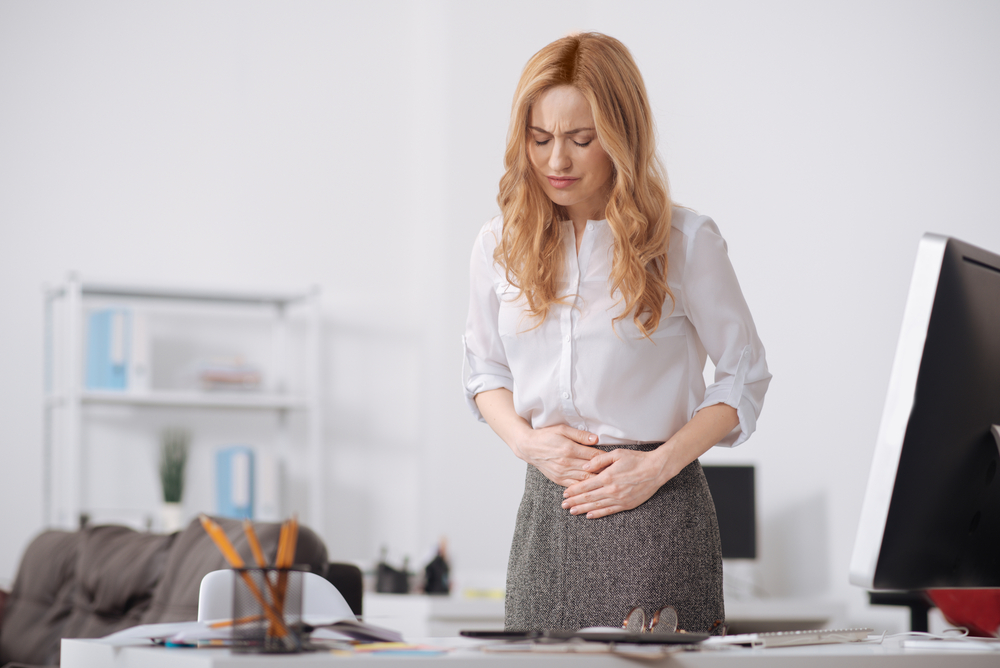
Adenomyosis is a disease that causes many symptoms that women experience without understanding the cause. Women just accept that their period is painful without realizing it is due to a disorder. This disease affects the uterus and can lead to infertility and other issues. Adenomyosis is often misdiagnosed as other conditions, such as fibroids or endometriosis.
Adenomyosis can be managed with medication and other treatments that help relieve symptoms such as pelvic floor physical therapy. This blog post discusses Adenomyosis and how to manage its symptoms so you can live a healthier life! If you are experiencing these symptoms, seek medical help to determine if the pain in your lower abdomen, pelvic area, or back is due to this condition.
What is Adenomyosis
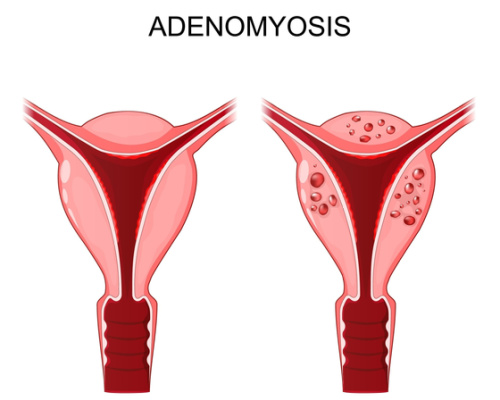
Adenomyosis is a condition where the uterus lining grows into the muscular wall of the uterus. This condition can cause painful periods, heavy bleeding during your period, prolonged bleeding, and abdominal pain. Women with adenomyosis have higher levels of pain during menstrual cycles. Adenomyosis can also lead to infertility.
How Common Is Adenomyosis?
This is a relatively rare condition, affecting about one in every 500 women. However, it is more common in older women. Adenomyosis occurs when the cells that line the uterus (endometrial cells) start to grow into the muscle of the uterus (myometrium).
What Causes Adenomyosis?
While there is no clear cause of Adenomyosis, estrogen seems to play a role in its development.
Listed below are several theories regarding its development:
Estrogen Influence
Adenomyosis is believed to be influenced by estrogen, a hormone that promotes the growth of the uterine lining (endometrium) during the menstrual cycle. It is thought that higher levels of estrogen or an imbalance between estrogen and progesterone may contribute to the development of adenomyosis.
Invasive Growth
One theory suggests that adenomyosis occurs when the endometrial tissue invades the myometrium, which is the muscular layer of the uterus. This invasive growth might result from disruptions in the boundary between the endometrium and myometrium, allowing the endometrial tissue to penetrate into the muscle layer.
Uterine Inflammation
Chronic inflammation in the uterus has been associated with adenomyosis. Inflammatory factors may cause changes in the uterine environment, leading to the development of adenomyosis.
Another theory suggests a link between adenomyosis and childbirth. Inflammation of the uterine lining during the postpartum period might cause a break in the normal boundary of cells that line the uterus. This disruption could potentially facilitate the invasion of the endometrial tissue into the muscular wall, contributing to the condition.
Understanding these potential mechanisms is crucial for developing targeted treatments and preventive strategies. While the exact cause remains unknown, ongoing research continues to explore these and other factors to provide clearer insights into adenomyosis.
Prior Uterine Surgeries
Some studies suggest that prior uterine surgeries, such as cesarean section or myomectomy (removal of uterine fibroids), may increase the risk of developing adenomyosis. These surgeries can disrupt the normal architecture of the uterus and potentially facilitate the infiltration of endometrial tissue into the myometrium.
Genetic Factors
There may be a genetic component to adenomyosis. Certain genetic factors could predispose individuals to develop the condition, although more research is needed to understand the specific genetic links.
Invasion of Bone Marrow Stem Cells
Emerging research suggests that the invasion of bone marrow stem cells into the uterine muscle (myometrium) may contribute to the development of adenomyosis. These stem cells, capable of differentiating into various cell types, including endometrial cells, may migrate to the uterus and integrate into the myometrium.
The Role of Hormones, Genetics, and Inflammation
Researchers don’t know why some people develop adenomyosis or what causes it. However, some research suggests hormones, genetics, or inflammation/trauma may contribute to adenomyosis. This reinforces the theories outlined above, highlighting the complex nature of this condition.
While there is no definitive cause of adenomyosis, it is likely a combination of hormonal, genetic, and inflammatory factors. Understanding these potential contributors can help in managing and potentially lessening the impact of adenomyosis.
Risk Factors
While adenomyosis can affect any woman, there are certain factors that may increase the risk of developing the condition. These risk factors include:
Age
Many wonder if adenomyosis is common in younger women. Current research suggests that the condition might be common in younger women. However it is more common in women over 30, and particularly in those over 40.
This indicates a broader age range of potential sufferers than previously believed, highlighting the importance of awareness and early diagnosis across all age groups.
Understanding the prevalence of adenomyosis across different age groups can help in better managing and diagnosing the condition, ensuring that women of all ages receive the necessary care and attention.
Childbirth
Women who have had multiple pregnancies or given birth at a young age may be at higher risk of developing adenomyosis.
Uterine surgeries
Women with uterine surgeries, such as a myomectomy or cesarean section, may be at increased risk of developing adenomyosis.
Endometriosis
Women with endometriosis may be at higher risk of developing adenomyosis.
Estrogen dominance
Women with higher levels of estrogen or an imbalance between estrogen and progesterone may be at increased risk of developing adenomyosis.
How Adenomyosis Affects Middle-Aged Women vs. Younger Women
Adenomyosis, a condition influenced by estrogen, affects women differently depending on their age group.
Middle-Aged Women:
- Age Group: Typically found in women in their 40s and 50s.
- Estrogen Exposure: These women have a prolonged exposure to estrogen, making them more susceptible to the condition.
- Severity: The intensity of adenomyosis symptoms in middle-aged women can often be more pronounced due to the cumulative effect of long-term estrogen exposure.
Younger Women:
- Age Group: Increasingly diagnosed in women under 40.
- Estrogen Exposure: Although they have had less exposure to estrogen, current studies indicate that adenomyosis is still relatively common.
- Severity: Younger women may experience a different set of symptoms or less severe manifestations, though this can vary widely among individuals.
Living with Adenomyosis
Adenomyosis can be challenging to manage. Understanding the full scope of the condition and complications that can arise from adenomyosis is crucial for effective management and can significantly improve your quality of life.
Detailed below are a few complications that can arise from adenomosis and some notable things to know when living with adenomyosis:
Adenomyosis Gets Worse Over Time
Adenomyosis is a progressive disease, which means that it may get worse over time. This is a chronic condition that needs to be managed. If left untreated, it may lead to infertility or other problems such as pelvic organ prolapse.
As women continue to live longer lives, reproductive issues like adenomyosis have increased in prevalence over the last 30 years. This is due to hormonal changes from menstruation, pregnancy, childbirth, and menopause over a longer lifetime.
Infertility Issues
Infertility is a symptom for some women because it will prevent implantation from occurring on the uterus wall. As endometrial tissue, which lines the uterus, grows into the muscular wall of the uterus, it makes it difficult for an embryo to implant. This silent condition can also cause miscarriages and premature births.
If you are experiencing infertility and have not been diagnosed with adenomyosis, it is important to see a gynecologist for testing. Adenomyosis is also more common in women who have had multiple pregnancies and c-sections.
Impact on Pregnancy
Adenomyosis is more common in women who have had multiple pregnancies and c-sections, but it can also make it harder to conceive, whether for the first time or when trying for another child. If you do become pregnant, adenomyosis can increase the risk of complications like:
- Miscarriage: The abnormal growth of endometrial tissue can interfere with the normal development of a pregnancy.
- Premature labor: The condition may lead to early contractions and labor, which can be risky for both mother and baby.
Adenomyosis occurs most often in women who are over 40 years old, so luckily, the majority of women will be done having children.
Understanding these risks can help women better prepare and seek the right medical care during pregnancy. If you are experiencing infertility and have not been diagnosed with adenomyosis, it is important to see a gynecologist for testing.
Adenomyosis Belly
You may have heard of the term adenomyosis belly. This nickname describes how adenomyosis can make the abdomen protrude as the uterine wall grows thicker. Adenomyosis belly may even make some women look like she is months into a pregnancy.
Anemia
Heavy bleeding may also lead to anemia in some women. If you feel cold or chronically fatigued, your body may not have enough iron-rich blood cells due to excess blood loss during menstruation.
Prolonged, heavy bleeding during your periods, a common symptom of adenomyosis, can significantly contribute to the development of chronic anemia. This condition can cause persistent fatigue and other health issues, as your body struggles to produce enough healthy red blood cells to replace those lost.
Health Problems Arising from Adenomyosis-Induced Anemia
Experiencing prolonged and heavy bleeding due to adenomyosis can lead to chronic anemia. This condition doesn’t just sap your energy; it brings a host of other health problems.
Managing chronic anemia caused by adenomyosis involves more than just addressing the symptoms. Consult with your healthcare provider for comprehensive treatment options, and take steps to mitigate these potential health issues.
Fatigue and Weakness
Chronic anemia diminishes red blood cell count, leading to insufficient oxygen transport throughout your body. This can make you feel constantly tired and weak, impairing your productivity and daily activities.
Shortness of Breath
With less oxygen circulating, your body has to work harder to accomplish regular tasks, often resulting in shortness of breath. Even mild physical exertion might leave you feeling winded.
Heart Issues
Your heart may need to pump more vigorously to compensate for the reduced oxygen-carrying capacity of your blood, potentially leading to heart enlargement or even heart failure over time.
Cognitive Difficulties
Low oxygen levels can affect your brain as well, causing problems with concentration and memory. You may find it harder to stay focused or retain new information.
Immune System Weakness
Anemia can compromise your immune system, making you more susceptible to infections. An opportunistic illness might take longer to recover from, further weakening your overall health.
Dizziness and Headaches
Reduced blood flow to the brain often results in frequent headaches and dizziness. These symptoms can interfere with your ability to perform routine tasks, affecting your quality of life.
Lifestyle Disruptions
The pain and excessive bleeding associated with adenomyosis can disrupt your lifestyle. You might avoid activities you’ve enjoyed in the past because you’re in pain or worry about sudden bleeding.
Understanding Adenomyosis: Can it Resolve on Its Own?
Adenomyosis is a condition where the inner lining of the uterus breaks through the muscle wall of the uterus. It can cause heavy periods, severe cramps, and other uncomfortable symptoms. The question many ask is whether adenomyosis can resolve on its own.
Natural Resolution After Menopause
For many women, adenomyosis tends to improve after menopause. This is because the condition is heavily influenced by hormonal changes, particularly estrogen. After menopause, the production of estrogen decreases significantly, leading to a natural reduction in symptoms. In some cases, adenomyosis may resolve entirely once menopause is reached.
Factors Influencing Symptom Resolution
While menopause offers a natural path to resolution for many, it’s essential to consider that each case is unique. Factors such as overall health, severity of the condition, and individual hormonal balance play critical roles in how adenomyosis progresses and eventually resolves.
Treatment Options Prior to Menopause
For those not yet near menopause or experiencing severe symptoms, several treatment options are available:
- Medications: Hormonal treatments can help manage symptoms by regulating the menstrual cycle and reducing heavy bleeding.
- Non-hormonal medications: Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs can alleviate discomfort.
- Surgical options: In more severe cases, procedures like endometrial ablation or even hysterectomy may be recommended.
While adenomyosis often resolves on its own post-menopause due to hormonal changes, symptom management and treatment are crucial for those still experiencing menstrual cycles. By consulting with a healthcare provider, you can explore the best course of action tailored to your specific needs.
Adenomyosis Symptoms
The symptoms of Adenomyosis are often misdiagnosed as other conditions, or left undiagnosed altogether. Adenomyosis is often referred to as the ‘Silent Disease’ because you may have no symptoms or it can be misdiagnosed for years before being discovered.
The symptoms are similar to other diseases and health problems, but there are some key signs that you may have Adenomyosis:
- Pelvic pain, especially during menstruation
- Heavy periods
- Painful sex
- Bloating and/or swelling in the stomach area
- Urinary problems
- Painful intercourse
- Severe cramping with knifelike pelvic pain
- Infertility
- Abnormal menstruation
- Enlarged uterus
In addition to this, the condition can also affect bowel and bladder function, resulting in:
- Leg pain
- Headaches
- Ovulation pain
- Nausea
- Fatigue
- Lightheadedness, dizziness, fainting
- Shortness of breath
When to See a Doctor About Adenomyosis
Knowing when to reach out to a healthcare provider is key if you’re dealing with adenomyosis. Watch for these symptoms that may require professional attention:
- Extremely heavy menstrual bleeding: If you’re soaking through pads or tampons every hour, that’s a sign something isn’t right.
- Severe menstrual cramps: Pain that interferes with your daily life needs to be checked by a doctor.
- Pain during intercourse: Discomfort during sex could be related to adenomyosis or other health issues.
- Persistent abdominal discomfort: A feeling of fullness or pressure in your lower abdomen might indicate complications.
Don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare provider if you experience any of these symptoms. Early intervention can make a big difference in managing your condition.
Diagnosing the Condition
A diagnosis usually begins with a physical exam and a review of your medical history. The doctor will ask about your menstrual cycle, including when you first started menstruating and when your last period was. They may also do a pelvic exam to check for enlarged or tender ovaries. Based on your symptoms, your gynecologist can do a few additional tests.
-
Pelvic Exam: During a pelvic exam, your provider may notice that your uterus has gotten larger, softer, or painful to the touch. These physical changes can be early indicators of adenomyosis.
-
Ultrasound:
A transvaginal ultrasound may be used to see if the uterine muscle is thickening. Although an ultrasound might not provide a very high-resolution image of the myometrium, it can help rule out other conditions, such as endometriosis or uterine fibroids.
- Imaging scans: If your doctor is uncertain about the diagnosis, they may order an MRI or CT scan to get a better look at the uterus. MRI is especially useful as it provides incredibly high-resolution images and shows the thickness of the endometrial-myometrial junction, helping to confirm if tissue is invading both layers. This can also show thickening walls in the uterus.
- Laparoscopy: A laparoscopy is an invasive procedure in which a small camera is inserted into the abdomen through a tiny incision. This allows the doctor to see if there are any lesions or fibroids inside the uterus.
- Biopsy: Adenomyosis is diagnosed with a biopsy of the uterine muscle. This involves taking a tissue sample from inside your uterus and sending it to a lab for testing. Unfortunately, this can only be done after a hysterectomy, so it isn’t a good option if you are not done having children.
Adenomyosis vs. Endometriosis vs. Uterine Fibroids
Endometriosis, adenomyosis, and uterine fibroids are all gynecological conditions that primarily affect women of reproductive age, involving the abnormal growth of endometrial tissue or other uterine issues. While they share some similarities, they also have distinct characteristics that set them apart. Here is a comparison highlighting the similarities and differences between endometriosis, adenomyosis, and uterine fibroids:
Similarities:
- Origin: Both endometriosis and adenomyosis involve the growth of endometrial tissue outside its usual location. Uterine fibroids, however, are benign tumors that grow within or on the uterus.
- Symptoms: They can cause similar symptoms, including pelvic pain, menstrual irregularities, and painful intercourse.
- Impact on fertility: All three conditions can contribute to infertility or difficulty conceiving.
- Hormonal influence: Hormones, particularly estrogen, play a role in the development and progression of all three conditions.
- Diagnosis: Endometriosis, adenomyosis, and uterine fibroids can all be challenging to diagnose accurately, often requiring imaging techniques such as ultrasound, MRI, or laparoscopy.
Differences:
- Location: Endometriosis occurs when endometrial tissue implants outside the uterus, commonly on the pelvic organs or abdominal cavity. Adenomyosis is characterized by the presence of endometrial tissue within the muscular wall of the uterus itself. Uterine fibroids are solid masses of cells that grow on different parts of the uterus.
- Tissue involvement: Endometriosis typically involves the formation of lesions or implants. Adenomyosis causes the infiltration of endometrial tissue into the uterine muscle. Uterine fibroids involve the growth of benign tumors.
- Symptoms: Adenomyosis often leads to more severe and prolonged menstrual bleeding, along with increased uterine enlargement and tenderness. Endometriosis may cause pain throughout the menstrual cycle. Uterine fibroids can cause heavy bleeding, frequent urination, and abdominal pain but do not involve the infiltration of endometrial tissue.
- Spread: Endometriosis can spread to various sites in the body, while adenomyosis remains confined to the uterus. Uterine fibroids remain localized to the uterus but can vary in size and number.
- Treatment: Although some treatment options overlap, the management strategies for these conditions can differ. Hormonal therapies, pain management, and surgery are commonly used for endometriosis. Adenomyosis may require more invasive procedures such as hysterectomy or uterine artery embolization to alleviate symptoms. Uterine fibroids may be treated with medications, non-invasive procedures, or surgical options like myomectomy or hysterectomy.
Comparing Adenomyosis and Endometriosis
Adenomyosis and endometriosis are disorders that involve endometrial-like tissue and can both be painful. The primary difference between these conditions lies in the location of the tissue growth:
- Adenomyosis: Endometrial-like tissue grows into the muscle of your uterus.
- Endometriosis: Endometrial-like tissue grows outside your uterus in places like your ovaries or fallopian tubes.
While adenomyosis is more likely to cause heavy menstrual bleeding, endometriosis may cause pain throughout the menstrual cycle. Both conditions can significantly impact quality of life and may require tailored treatment approaches, including hormonal therapies and surgical interventions.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management plan, as each individual’s symptoms and treatment options can vary.
Can Adenomyosis Become Cancerous?
Adenomyosis, a benign condition, does not transform into cancer. It involves the growth of endometrial tissue within the muscular walls of the uterus, causing symptoms like heavy menstrual bleeding and pelvic pain. However, it’s essential to note that while adenomyosis itself is non-cancerous, it may coexist with other conditions.
Symptoms to Monitor:
- Heavy or prolonged menstrual periods
- Severe cramping and pelvic pain
- Enlarged and tender abdomen
Treatment Options:
- Medications for pain relief and to control bleeding
- Hormonal treatments to manage symptoms
- Surgical options, like hysterectomy, in severe cases
Differentiating from Cancer
Adenomyosis, where the inner lining of the uterus grows into the muscle wall, is not linked to cancer. Although it can cause significant discomfort, including heavy menstrual bleeding and pelvic pain, it remains a benign (non-cancerous) condition.
It’s important to distinguish adenomyosis from other uterine conditions like endometriosis or fibroids. While these conditions also don’t lead to cancer, they share similar symptoms.
For peace of mind and proper management, regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are recommended. Gynecological exams and appropriate imaging tests help differentiate adenomyosis from malignant conditions such as endometrial or uterine cancer.
Diagnostic Tools include:
- Ultrasound
- MRI
- Blood tests
What’s the Outlook for Someone with Adenomyosis?
Adenomyosis can be painful and disruptive, but it’s generally not life-threatening.
Long-Term Outlook:
- Natural Resolution: The condition typically improves after menopause, offering relief to many women as they get older.
- Potential Complications: Before menopause, though, adenomyosis can cause significant discomfort and may lead to other health problems if it’s not treated.
How to Treat Adenomyosis
There is no known cure for adenomyosis, but there are treatments available that can help lessen the symptoms. These symptoms can be uncomfortable, so if you suspect that you have it, make an appointment with your doctor. Adenomyosis is often difficult to diagnose because of its similar symptoms to other conditions, but once diagnosed the best treatment options are available.
Some treatments that may help relieve adenomyosis:
- Pain medication: Taking medications to reduce pain and inflammation can ease cramping. These include over-the-counter NSAIDs and naproxen.
- Hormone therapy: If your doctor thinks that the adenomyosis is being caused by high levels of estrogen, they may prescribe hormone therapy. This will help to lower estrogen levels and can be done with medication or surgery.
- Nonhormonal medication: Medications like tranexamic acid can reduce the amount of vaginal bleeding, providing relief from one of the most common symptoms of adenomyosis.
- Heating pads: These can reduce pain and pressure in the uterus as a temporary fix.
- Surgery: If other treatments haven’t worked, surgical options may be considered.
- Adenomyomectomy: This surgery removes adenomyosis from your uterine muscle, preserving the uterus.
- Hysterectomy: This procedure fully removes the uterus and is only an option if you are done having children. After a hysterectomy, you won’t have a menstrual cycle or be able to get pregnant.
Because the hormone estrogen promotes endometrial tissue growth, adenomyosis symptoms often go away after menopause. Until then, these treatments can help manage pain, heavy bleeding, and other symptoms effectively.
Essential Questions to Ask Your Healthcare Provider About Adenomyosis
Navigating a diagnosis of adenomyosis can be daunting, but having a list of questions prepared can help you manage your condition better. Here are some important questions to consider:
Understanding the Condition
- How did adenomyosis develop in my case?
- Are there any factors that made me more susceptible to this condition?
Treatment Options
- What are the most effective treatments available for adenomyosis?
- Are there any non-surgical options I should consider first?
Impact on Fertility
- How might adenomyosis affect my ability to get pregnant?
- What fertility treatments, if any, are beneficial for someone with adenomyosis?
Birth Control Choices
- Should I consider changing my current method of birth control?
- Are there birth control options better suited for individuals with adenomyosis?
Monitoring and Managing Symptoms
- What symptoms should I monitor closely?
- Are there signs of complications I need to be aware of?
Long-Term Management
- How will adenomyosis impact my long-term health?
- Are there lifestyle changes I should implement to manage this condition better?
Support and Resources
- Can you recommend resources or support groups for patients dealing with adenomyosis?
- How often should I schedule follow-up appointments to monitor this condition?
Having these questions ready can not only provide clarity about your condition but also empower you to take an active role in managing your health. Don’t hesitate to ask your healthcare provider for detailed explanations and additional resources to support your journey.
Prevention
There is no clear cause of Adenomyosis, so there are no known ways to prevent Adenomyosis. However, seeking medical treatment and diagnosis early can help manage the symptoms and improve quality of life. To better understand the underlying cause of your pain, it is important to seek medical attention.
How Can I Prevent Adenomyosis?
While the exact cause of adenomyosis remains unclear, certain lifestyle choices and health practices may help reduce the risk:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity is often linked with various hormonal imbalances, which might increase the risk of adenomyosis. Stay active and follow a balanced diet to keep your weight in check.
- Exercise Regularly: Engaging in regular physical activity can help regulate your hormones and improve overall reproductive health.
- Manage Stress: High-stress levels can disrupt hormone function. Practice stress-relief techniques like yoga, meditation, or mindfulness to promote emotional and physical well-being.
- Monitor Menstrual Health: Keeping track of your menstrual cycle can help you spot any irregularities early. Addressing these issues promptly with your healthcare provider may help in managing risks.
- Limit Estrogen Exposure: Certain environmental factors, such as exposure to estrogen-like chemicals found in some plastics and personal care products, could potentially impact hormonal balance. Aim to use more natural and organic products whenever possible.
- Consult Your Healthcare Provider: Regular check-ups and open communication with your healthcare provider can go a long way. They can offer personalized advice based on your health history and other risk factors.
While these steps can’t guarantee prevention, they may contribute to your overall health and potentially lower your risk of developing adenomyosis.
How to Manage Adenomyosis at Work
Adenomyosis can present significant challenges in the workplace due to symptoms like debilitating pain and fatigue. However, with the right strategies, you can manage your condition effectively while maintaining your productivity and well-being. Here are some tips on how to manage adenomyosis at work:
Understand Your Condition
Educate yourself about adenomyosis to better understand your symptoms and triggers. Knowing your condition will help you anticipate flare-ups and manage your symptoms more effectively. Although not harmful, the pain and excessive bleeding associated with adenomyosis can disrupt your lifestyle. You might avoid activities you’ve enjoyed in the past because you’re in pain or you worry that you might start bleeding.
Open Communication
Consider informing your employer or HR department about your condition. While it might be a difficult conversation, being open can lead to necessary accommodations that make your work life more manageable.
Flexible Working Arrangements
Request flexible working arrangements to accommodate your needs, such as:
- Work-from-home options: Working from home on days when symptoms are severe can help you manage your condition better.
- Flexible hours: Starting and finishing work at different times can help you manage pain and fatigue throughout the day.
- Reduced hours: If feasible, temporarily reducing work hours during flare-ups can help manage symptoms without adding undue stress.
Ergonomic Workspaces
Set up an ergonomic workspace to reduce discomfort:
- Adjustable chairs and desks: To minimize strain and allow for frequent position changes.
- Supportive cushions or pads: To alleviate pressure and discomfort.
- Standing desks: To provide the option to alternate between sitting and standing.
Utilize Wellness Programs
Take advantage of any wellness programs offered by your employer:
- Access to mental health resources: Counseling or therapy sessions can help manage the emotional toll of chronic pain.
- Physical well-being initiatives: Programs like yoga or gentle exercise classes can aid in managing symptoms and improving overall health.
Seek Medical Support
Stay on top of your medical treatments and appointments:
- Medication management: Ensure you have access to any prescribed medications and take them as directed.
- Doctor visits: Schedule regular appointments with your healthcare provider to monitor and manage your condition.
Join Support Groups
Consider joining online or local support groups for adenomyosis:
- Emotional support: Connecting with others who have similar experiences can help you gain valuable insights and tips for managing your condition from others who understand what you’re going through.
By taking these steps, you can better manage your adenomyosis while maintaining your productivity and well-being at work. It’s important to advocate for your needs and utilize available resources to create a supportive work environment.
Get Help From Dr. Lodge in Cool Springs, TN
If you are experiencing any of the symptoms associated with adenomyosis, schedule an appointment with your gynecologist. Dr. Lodge in Cool Springs, TN can help diagnose and treat the condition. Adenomyosis is a difficult disease to live with, but there are treatments available that can make your life easier. Don’t suffer in silence – get help today.